|
All checks were successful
ci/woodpecker/push/woodpecker Pipeline was successful
|
||
|---|---|---|
| benches | ||
| docs | ||
| examples | ||
| scripts | ||
| src | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitlab-ci.yml | ||
| .woodpecker.yml | ||
| Cargo.toml | ||
| LICENSE-APACHE2 | ||
| LICENSE-MIT | ||
| README.md | ||
Cyclic Poly
This crate is an implementation of the hashing algorithm given in Section 2.3 of the paper:
Jonathan D. Cohen, Recursive Hashing Functions for n-Grams, ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 15 (3), 1997.
Other opensource implementations from this paper usually concentrate on other algorithms that appear in later sections.
This hashing algorithm has features that stand out in comparison to other hashing algorithms:
- The algorithm supports recurrent/rolling hash calculations.
- The rolling hash calculation is around 5 times faster than Adler32.
- Hash values are decomposable.
Recurrent/Rolling
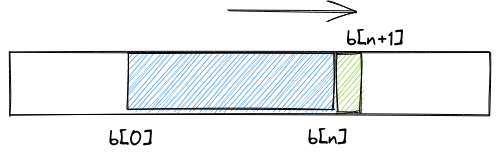
A rolling hash (sometimes called a recurrent hash), can calculate a new hash value from a previous hash value and a small change in the data. Rolling hashes are useful to hash a window of data that slides along a collection of data:
This is much faster than recalculating a hash value for every block.
Rolling hashes are an efficient way for finding a block of data that has a given hash value.
Decomposable
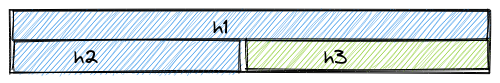
A decomposable hash, can calculate a hash value for a block of data given a hash value for a bigger block of data and the hash value for the remaining data:
In the example above, the hash `h_3` can be calculated from the hashes `h_1` and `h_2`.
Alternative Algorithms
The Adler32 hash/checksum algorithm can be used as a rolling hash and was made popular by the zlib library and rsync tool.
Performance
Performance comparisons were done on a laptop and are relative to the adler32 crate. To run this comparison execute cargo bench.
Single block
The Cyclic Polynomial hashing is slower than Adler32 when hashing a single block.
| Algorithm | MB/sec |
|---|---|
| Cyclic Poly 32bit | 2127 |
| Cyclic Poly 64bit | 2126 |
| Adler32 | 2562 |
Rolling
The calculation of rolling hashes is faster than Adler32.
| Algorithm | MB/sec |
|---|---|
| Cyclic Poly 32bit | 1254 |
| Cyclic Poly 64bit | 1048 |
| Adler32 | 170 |
Collisions
To calculate hash collisions on random data execute:
cargo run --example collisions
This will output the number of collisions.
| Algorithm | Collisions |
|---|---|
| Random Number Generator | 118 |
| Cyclic Poly 32bit | 140 |
| Adler32 | 2872 |
Cargo Features
std
By default, this crate uses the Rust standard library enabled with the feature std . The crate supports no_std if it is included as a dependency without default features e.g.:
cyclic-poly-23 = { version = "xxx", default-features = false }